
The descriptions should be brought to class. A one-sentence description of a recent event will serve if it permits them to reexperience the event. Kerry Maida, Mary Summo (eds.), "9 - Peripheral Nervous System", Netter's Atlas of Neuroscience (Third Edition), Philadelphia: Elsevier, pp. 153–231, doi: 10.1016/b978-1-9.A day or more before the demonstration, ask the students to write a very brief description of a situation that had made them feel very angry or fearful. Kerry Maida, Mary Summo (), Felten, David L. : CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list ( link) Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville MD, Bethesda Usa, 20894 (). ^ Information, National Center for Biotechnology Pike, U.For vertebrates, however, the response of a skeletal striated muscle fiber to a neurotransmitter – always acetylcholine (ACh) – can only be excitatory. In invertebrates, depending on the neurotransmitter released and the type of receptor it binds, the response in the muscle fiber could either be excitatory or inhibitory. Some reflex responses, such as withdrawing the hand after touching a hot surface, are protective, but others, such as the patellar reflex ("knee jerk") activated by tapping the patellar tendon, contribute to ordinary behavior. The next simplest reflex arc is a three-element chain, beginning with sensory neurons, which activate interneurons inside of the spinal cord, which then activate motor neurons. The singular example of a monosynaptic reflex is the patellar reflex. Reflex circuits vary in complexity-the simplest spinal reflexes are mediated by a two-element chain, of which in the human body there is only one, also called a monosynaptic reflex (there is only one synapse between the two neurones taking part in the arc: sensory and motor). Stimuli from the precentral gyrus are transmitted from upper motor neurons, down the corticospinal tract, to lower motor neurons ( alpha motor neurons) in the brainstem and ventral horn of the spinal cord: upper motor neurons release a neurotransmitter called glutamate from their axon terminal knobs, which is received by glutamate receptors on the lower motor neurons: from there, acetylcholine is released from the axon terminal knobs of alpha motor neurons and received by postsynaptic receptors ( nicotinic acetylcholine receptors) of muscles, thereby relaying the stimulus to contract muscle fibers.Ī reflex arc is a neural circuit that creates a more or less automatic link between a sensory input and a specific motor output. The basic route of nerve signals within the efferent somatic nervous system involves a sequence that begins in the upper cell bodies of motor neurons ( upper motor neurons) within the precentral gyrus (which approximates the primary motor cortex). The somatic nervous system controls all voluntary muscular systems within the body, and the process of voluntary reflex arcs. ( May 2021) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message) Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. They include smell, eye muscles, mouth, taste, ear, neck, shoulders, and tongue. Cranial nerves: They are the nerve fibers that carry information into and out of the brain stem.Spinal nerves: They are mixed nerves that carry sensory information into and motor commands out of the spinal cord.
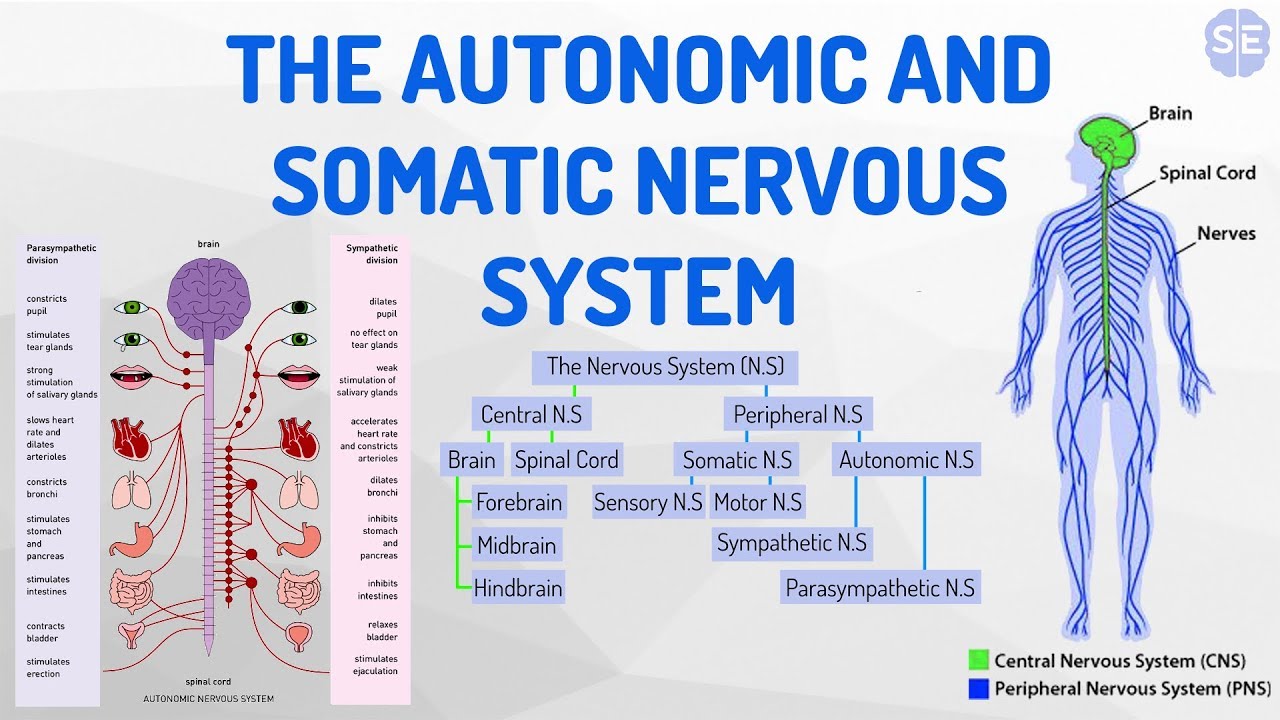

Thus the somatic nervous system consists of two parts: Besides these, thousands of association nerves are also present in the body. In the body, 31 segments of nerves are in the spinal cord and 12 are in the brain stem. With each segment, there is a pair of sensory and motor nerves. There are 43 segments of nerves in the human body. The a- of afferent and the e- of efferent correspond to the prefixes ad- (to, toward) and ex- (out of). The somatic nervous system consists of sensory nerves carrying afferent nerve fibers, which relay sensation from the body to the central nervous system (CNS), and motor nerves carrying efferent nerve fibers, which relay motor commands from the CNS to stimulate muscle contraction. The somatic nervous system ( SNS), or voluntary nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system associated with the voluntary control of body movements via skeletal muscles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
